Are Snails Amphibians? Discover the captivating global of snails and their distinct type in this comprehensive manual. Unravel myths, discover their specific lifecycle and environmental roles, and discover how these fascinating creatures fluctuate from amphibians.
Introduction
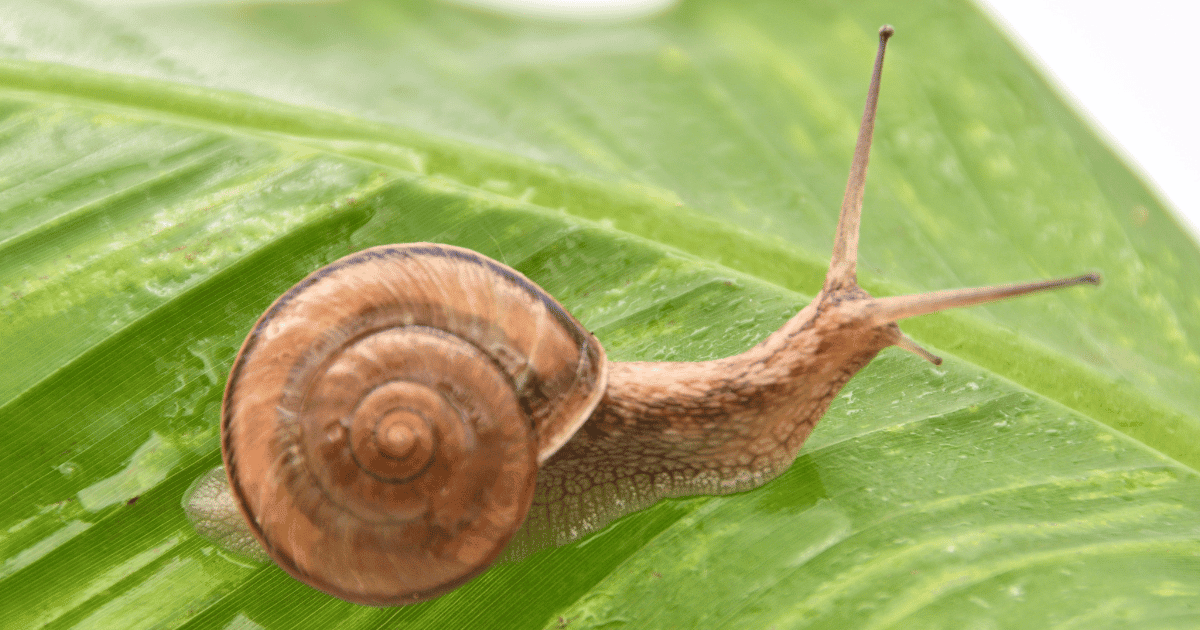

Have you ever wondered about the charming global of animals and their classifications? In this text, we delve right into a customarily asked question: are snails amphibians? This subject matter piques the curiosity of nature enthusiasts and sheds light on the importance of expert animal classifications. It’s vital to apprehend the differences and similarities amongst various species to appreciate the range of lifestyles on our planet. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery to get to the bottom of the mysteries of snails and amphibians.
Exploring the Definition of Amphibians
Amphibians are various groups of animals recognized for their particular lifestyle cycles and physical characteristics. Typically, they begin their lifestyles in water as larvae, respiration through gills, and later increase their lungs for respiration air as adults. Examples encompass frogs, salamanders, and newts. These creatures are outstanding through their moist, permeable pores and skin, critical in breathing. Understanding the defining tendencies of amphibians is essential to cope with our number one query, “Are Snails Amphibians?” By comparing those developments with the ones of snails, we will decide the accuracy of this classification.
Understanding Snails: A Brief Overview
Fascinating in their personal property, snails are recognized for their gradual movement and one-of-a-kind shells. They belong to the Gastropoda class, making them one of the most diverse organizations in the mollusk species. Snails can be found in several environments, from gardens and forests to rivers and oceans. Their physical traits encompass a tender, unsegmented frame and a problematic spiral shell, providing protection and shelter. This phase aims to provide readers with a clean know-how of what snails are, setting the level for evaluating them as amphibians in our quest to answer, are snails amphibians?
Comparative Analysis: Snails vs. Amphibians
When comparing snails and amphibians, several key variations emerge as apparent. Physically, amphibians have clean, moist pores and skin, while snails have a hard shell. In terms of habitat, while many amphibians require watery surroundings at a few levels of their lifestyles, snails are more flexible, inhabiting numerous environments, including water, but no longer necessarily dependent on it. Amphibians typically undergo metamorphosis from a larval stage to a grownup shape, a process no longer found in snails. These differences are essential in addressing the middle question, are snails amphibians? and highlight the significance of knowledge of each organization’s specific characteristics.
The Biological Classification of Snails
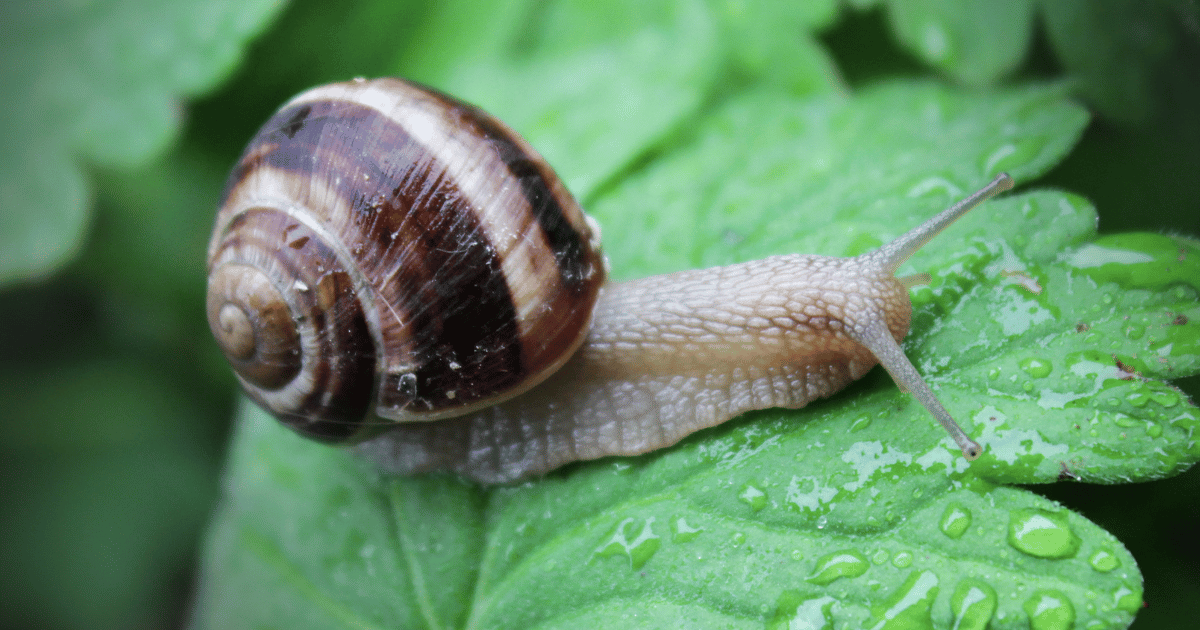
Diving deeper into the organic type, snails aren’t labeled as amphibians. They belong to the phylum Mollusca, which is excellent from the Amphibia phylum. This distinction is primarily based on numerous elements and their anatomical shape, reproductive methods, and developmental ranges. Snails, with their distinct shell and gastropod functions, vary extensively from the amphibian elegance. Understanding this classification is critical in dispelling the misconception embodied in the question, are snails amphibians? By examining the taxonomy of snails, we can respect their unique region within the animal state.
Common Misconceptions About Snails
There are several misconceptions surrounding snails, often stemming from a need for more understanding in their biological class. One familiar fable is that snails are closely associated with amphibians, which, as we have hooked up, is not the case. Another misconception is that every snail is sluggish; while many are, a few aquatic species can circulate highly quickly. Additionally, it is frequently notion that snails aren’t vital to the atmosphere, yet they play crucial roles, which include decomposers and food resources for different animals. Clarifying those misconceptions facilitates us to respect the particular nature of snails and, in addition, confirms the solution to the query, “Are Snails Amphibians?”
The Importance of Accurate Animal Classification
Accurate types of animals, like distinguishing between snails and amphibians, are critical for several motives. It aids in understanding ecological relationships, ensuring exemplary conservation efforts, and fostering educational focus. Classifying organisms efficiently enables scientists and conservationists to broaden techniques to defend biodiversity and preserve environmental stability. It also prevents misunderstandings that might lead to insufficient care or conservation of a species. This understanding reinforces the importance of our inquiry, Are Snails Amphibians? highlighting the broader implications of animal class.
Fascinating Facts About Snails
| Facts | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Age | Some species, like the Giant African Land Snail, can live up to 10 years or more in captivity. |
| Life Cycle | Snails go through a life cycle that includes egg, hatchling, juvenile, and adult stages. |
| Reproduction | Most snails are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs. |
| Habitat Variety | Snails can be found in diverse environments, from dense forests to arid deserts and freshwater bodies. |
| Diet | They primarily feed on plants, algae, and sometimes even small insects or decaying organic matter. |
| Size | Sizes vary greatly; the tiny garden snail may only reach up to an inch, while the Giant African Land Snail can grow up to 15 inches. |
| Senses | Snails have a highly developed sense of smell and can detect chemicals in their environment, aiding in finding food and mates. |
| Shell Coiling | The direction of shell coiling (left/right) is genetically determined and remains constant within a species. |
| Speed | Contrary to popular belief, some aquatic snails can move quite rapidly, while land snails generally maintain a slow pace. |
| Hibernation | Snails can enter a state of hibernation (or estivation in hot climates) for up to several years, reducing their metabolic rate significantly. |
Critical Differences Between Snails and Amphibians
The critical variations among snails and amphibians lie in their duplicate, body structure, and habitat diversifications. Amphibians typically lay eggs in water, which then go through metamorphosis, while maximum snails lay eggs on land, and their younger turn out to be miniature adults. Physiologically, amphibians breathe through their pores ski,n, and lungs, whereas snails breathe using gills or a lung-like organ, relying on the species. Habitat-clever amphibians want wet environments to continue to exist, not like snails, which are found in various habitats. These differences are vital in knowing why snails aren’t amphibians, offering a straightforward solution to the query, are snails amphibians?
Snails inside the Animal Kingdom: Where Do They Fit?
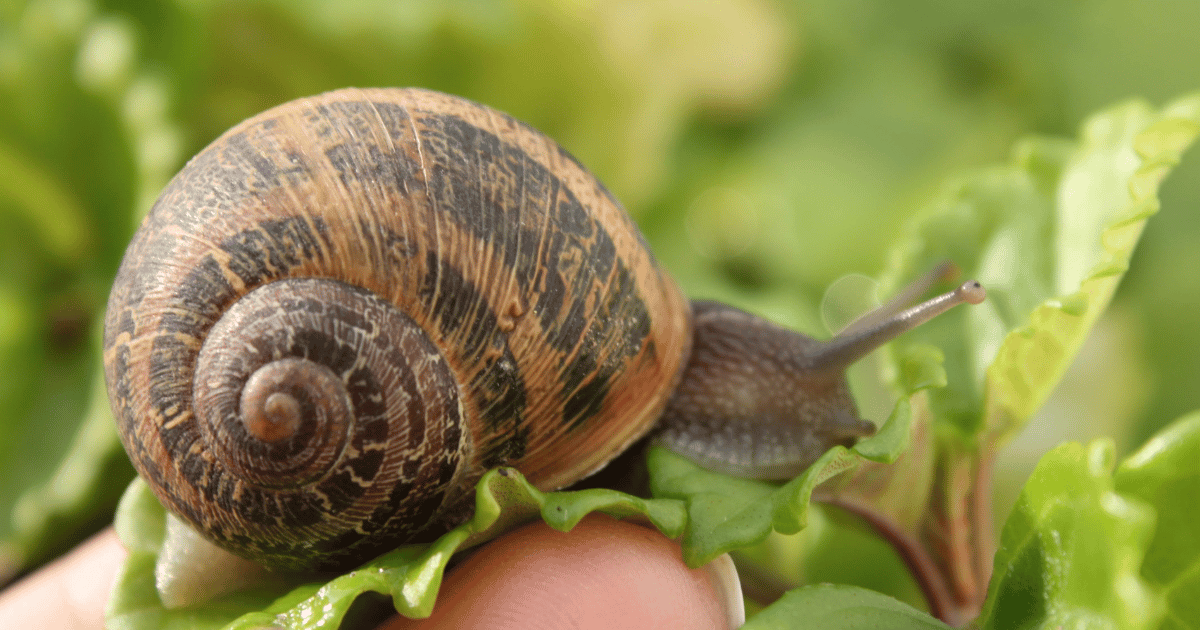

Snails occupy a unique function inside the animal state. As contributors to the phylum Mollusca and the class Gastropoda, they’re highly memorable from amphibians, which belong to the phylum Chordata, magnificence Amphibia. Snails are closely associated with different mollusks like clams and squids, sharing standard capabilities like a smooth frame and, in many cases, a shell. This classification underlines the variety inside the animal state and allows us to understand the distinct evolutionary paths of various species. It additionally definitively answers our primary question, are snails amphibians? by putting snails in their correct organic institution.
Environmental Impact of Snails and Amphibians
The environmental effect of both snails and amphibians is tremendous, even in exclusive ways. Snails are essential in ecosystems as decomposers, breaking down natural fabric and contributing to nutrient cycling. Some species also act as bioindicators, reflecting the fitness of their environment. Amphibians, alternatively, are essential for pest control, as many feed on bugs, and their permeable skin makes them touchy to environmental modifications, serving as signs of ecological health. Understanding these roles underscores the ecological importance of both companies and, in addition, distances snails from the amphibian classification, reinforcing the solution to are snails amphibians?
Conclusion
In the end, the question are snails amphibians? opens a charming window into the world of biological type. As we’ve explored, snails are incredibly exceptional from amphibians, belonging to the Mollusca phylum and showing particular traits and ecological roles. Understanding these differences depends not only on clinical accuracy but also on our appreciation and recognition of biodiversity. By debunking this common misconception, we take advantage of a deeper understanding of the natural world and its various lifestyle forms.
FAQs
Why are snails not considered amphibians?
Snails are a part of the Mollusca phylum, which differs from the Amphibia phylum to which amphibians belong.
What are the primary variations between snails and amphibians?
Key variations include their reproductive methods, respiratory mechanisms, and habitat necessities.
Can snails stay in the water and on land?
Yes, sure, snail species are aquatic, while others are terrestrial.
How do snails gain the environment?
Snails contribute to nutrient recycling as decomposers and function as meals for various animals.
Hello! I’m Javed, a versatile content writer specialized in various niches, with a particular passion for home and garden topics. My expertise extends beyond writing—I’m also skilled in SEO and WordPress development, boasting over four years of experience in these areas.

They helped me when no one else would get the services i needed
Awesome. Very clear. They are an awesome website. Will visit and use again!
First off I want to say terrific blog! I had a quick question in which I’d like to
ask if you don’t mind. I was interested to find out
how you center yourself and clear your mind before writing.
I’ve had a tough time clearing my thoughts in getting my thoughts out.
I do enjoy writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are
generally wasted simply just trying to figure out how to begin. Any ideas or hints?
Appreciate it!
GOOD AND CREATIVE.. CANT WAIT TELL MY HOMIES
Awesome. Very clear. They are an awesome website. Will visit and use again!
They give good quality work and always willing to work with you.
Actually really nice, great group of individuals.